What Function Does Atp Carry Out in Living Things
ATP is used by cells to store and transport chemical energy. Identifies DNA start sequences for transcription D.

Concept Map Tutorial How To Create Concept Maps To Visualize Ideas Concept Map Template Concept Map Cellular Respiration
Inside every cell of all living things energy is needed to carry out life processes.

. Cellular respiration stores ATP while photosynthesis releases ATP. The cells take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide. What function does ATP carry out in living things.
What function does ATP carry out in living things. Helps maintain the fluidity of cell membranes How are cellular respiration and photosynthesis related in terms of energy. This happens in the cells so it is also called cellular respiration.
What function does ATP carry out in living things. Aids in protein folding and coiling B. The removal of a phosphate group.
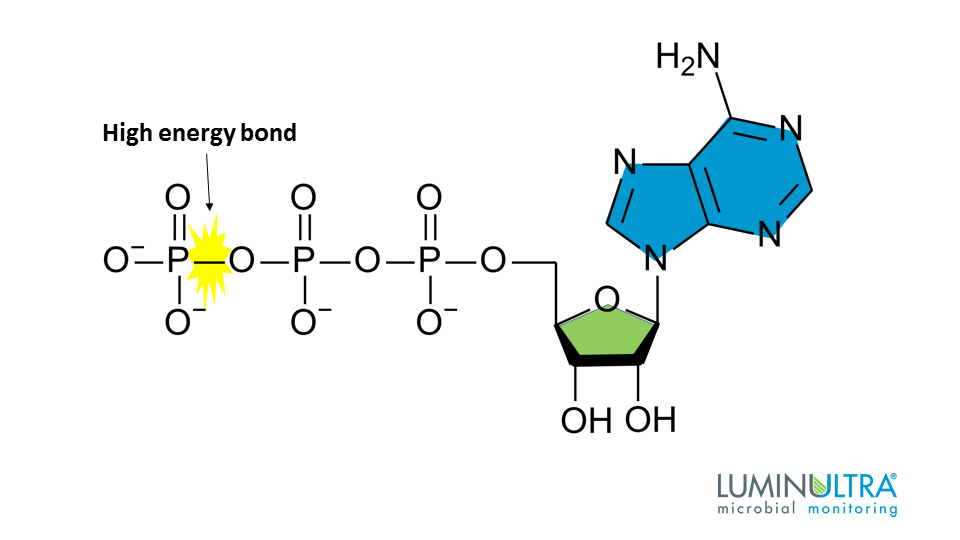
ATP stores chemical energy in the bonds that holds its phosphate molecules and releases the energy when this bond is broken. Identifies DNA start sequences for transcription D. Adenosine triphosphate commonly known as ATP is the energy currency for chemical reactions in living cells.
Like a car cells can run out of energy ATP. Aids in protein folding and coiling B. ADP is used to couple chemical reactions that woud otherwise not.
Used to capture and transfer energy C. Organisms use a high energy molecule called ATP Adenosine Triphosphate as a fuel source. Aids in protein folding and coiling used to capture and transfer energy identies DNA start sequences for transcription helps maintain the ²uidity of cell membranes 60 seconds.
This form of respiration is called aerobic respiration. Other functions of ATP include supplying the energy required for the muscle contraction circulation of blood. One oxygen to carbon.
When the bond between the second and third phosphate of ATP is broken. When ATP is synthesized into glucose C. However there are no ATP stations to fill up a cell with ATP.
So option B is correct. What is required for aerobic respiration. Cellular respiration produces oxygen while photosynthesis uses oxygen.
Helps maintain the fluidity of cell membranes. Helps maintain the fluidity of cell membranes. Aids in protein folding and coiling B.
ATP captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. What organisms carry out respiration in the carbon cycle. ATP is the most important biological molecule that provides chemical energy.
Energy is required to break down and build up molecules and to transport molecules across plasma membranes. ATP is used to both capture and to transfer cellular energy. As the cells run out of oxygen they switch to anaerobic respiration fermentation which allows the cell to make small amounts of ATP in the absence of oxygen.
The cells then use this energy to drive cellular functions. It is used to capture and transfer energy In which way are photosynthesis and cellular respiration different. Functions of ATP The ATP is used for various cellular functions including transportation of different molecules across cell membranes.
Which of the following results in the storage of energy in terms of the ATPADP cycle. When sunlight enters the leaf of a plant B. Photosynthesis releases energy while cellular respiration stores energy.
ATP must be re. Cellular respiration stores ATP while photosynthesis releases ATP. Adenosine triphosphate ATP energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things.
What Function Does Atp Carry Out In Living Things. ATP functions as the energy currency for cells. What function does ATP carry out in living things.
How are cellular respiration and photosynthesis related in terms of energy. All Living things need a source of energy to carry out their life functions. Used to capture and transfer energy C.
The addition of a phosphate group. ATP adenosine triphosphate corresponds to an unstable but high-energy compound that is generated by mitochondria by way of respiration and other processes. Plants have mitochondria and can perform cellular respiration.
What function does ATP carry out in living things. C ATP is used to capture and transfer chemical energy. All lifes work needs energy.
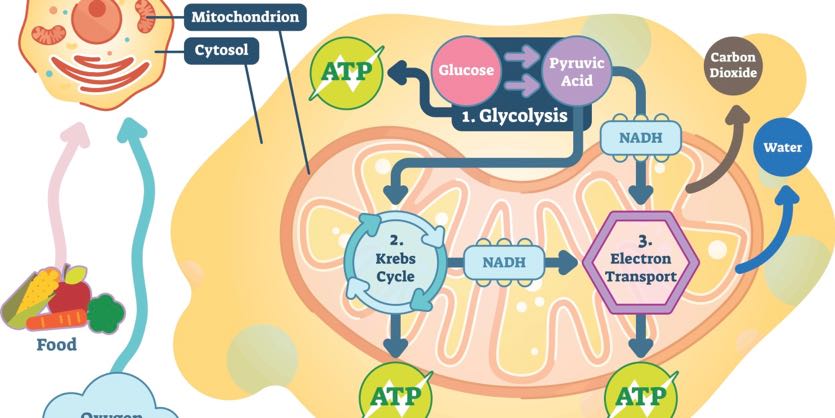
Respiration is the process that all living things go through to create the energy they need to live. It allows the cell to store energy briefly and transport it within the cell to support endergonic chemical reactions. This process releases carbon dioxide and water as waste products.
ATP in Living Systems. Cellular respiration is the process that occurs in the mitochondria of organisms animals and plants to break down sugar in the presence of oxygen to release energy in the form of ATP. The structure of ATP is that of an RNA nucleotide with three phosphates attached.
Yield energy in the form of ATP as it is passed down the respiratory chain act as an acceptor for electrons and hydrogen forming water. You might say it is the gasoline of the cell. In living things this molecule is concerned with energy transfer and capture such that organic molecules result from this activity due to its unstability.
What did the number boxes represented in the diagram. Photosynthesis releases energy while cellular respiration stores energy. Cellular respiration produces oxygen while photosynthesis uses oxygen.
When carbon dioxide joins with other carbon molecules D. ATP molecules function as the energy currency in living cells. Used to capture and transfer energy C.
How does ATP release energy. Identifies DNA start sequences for transcription D. The breaking of the bond between the 5-carbon sugar and the 1st phosphate group.
What function does ATP carry out in living things. As the cells run out of oxygen they die off gradually and the weightlifters muscles have fewer contracting muscle cells. Energy unlike matter cannot be recycled so organisms require a constant input of energy.
Combine with carbon forming CO2.

Energy Cycle From Plants To Animals Energy Transformations Oxygen Plant Energy

Atp In Living Systems Biology For Non Majors I

Adenosine Triphosphate Definition Structure Function Facts Britannica

Adenosine Triphosphate Wikipedia Atp Molekul Tattoo Muskelkontraktion Chemische Bindung

What Is Atp Biology Classroom Biology Molecular Biology

Cellular Aerobic Energy Production Also Known As Cellular Respiration Aerobic Oxidation And Oxidative Phosphorylation Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Oxidative Phosphorylation

Atp In Living Systems Biology For Non Majors I

Aerobic Respiration Is A Biological Process That Takes Energy From Glucose And Other Cellular Respiration Biochemistry Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration
Understanding Atp 10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered Ask The Scientists

Structure Of A Mitochondrion Mitochondria Are Organelles Of The Eukaryotic Cells That Provide The Energy For Th Celula Eucariota Celulas Procariotas Eucariota

Infographic The Hierarchy Of Life Plant And Animal Cells Biology Lessons Human Body Systems

Biology In Motion Atp And Energy Storage This Would Be A Nice Quick Activity That You Could Do As A Cl Biology Classroom Life Science Lessons Biology Lessons

Re Energize Your Cells Recharge Your Life The Mitochondria And Antioxidant Connection Science Biology Science And Nature Science Facts

Aerobic Respiration Bio Anatomical Vector Illustration Diagram Vectormine Mitochondria Oxidative Phosphorylation Aerobics

Cellular Respiration Biology Classroom Teaching Biology Biology Resources

Atp In Living Systems Biology For Non Majors I

3 Living Things Use Energy Life Science Science Middle School Science
What Is Atp Adenosine Triphosphate And What Does It Do

Image Result For Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Biology Classroom Photosynthesis
Comments
Post a Comment